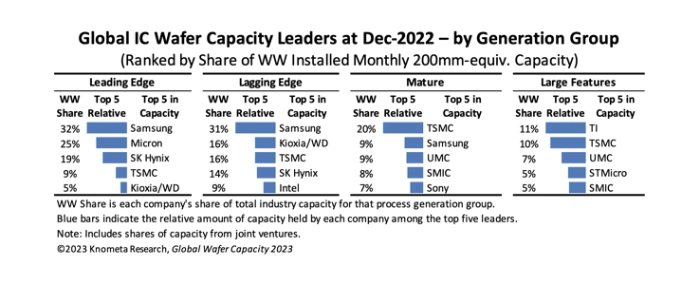
Samsung, Micron, and SK Hynix owns the bulk of leading-edge wafer capacity
76% of leading-edge capacity was held by Samsung, Micron, and SK Hynix at the end of 2022, with the majority going toward the development of advanced DRAM and 3D NAND.
The information comes Knometa Research's latest analysis of the IC industry's installed wafer capacity. In its new Global Wafer Capacity 2023 report, the researchers compiled data to identify the top companies in the segments of leading-edge, lagging-edge, mature, and large-feature technologies – and the data is clear; Samsung was, by far, the industry's biggest source of both leading- and lagging-edge capacity at the end of 2022.
Leading edge: Lagging edge: Mature: Large feature: |
In general, capacity was deemed leading-edge if the wafers were made using fine-geometry processes that had just recently entered mass manufacturing (the past two years).
Samsung was, as stated earlier, the biggest source of leading- and lagging-edge capacity at the end of last year. The South Korean company is the top supplier of DRAM and NAND flash memory products in the market and one of the biggest producers of advanced logic products, including SoCs for the fabless semiconductor sector and low-power, high-performance application processors for its own smartphones.
According to Knometa's research, the world's largest pure-play foundry, TSMC, placed among the top five businesses in each of the four process generation divisions. With 39 fab lines offering a diversified spectrum of process technologies, TSMC serves a wide range of clients. In the mature technology segment, other pure-play foundries like UMC and SMIC play important roles.
Texas Instruments was the biggest source of capacity for large-feature technologies at the end of the year, leading the market in analog and analog-centric mixed-signal ICs. STMicroelectronics is one of the largest manufacturers of analog and microcontroller products, which are commonly produced with mature and large-feature processes.


