TPCA: Global flexible PCB market rebounds in 2024
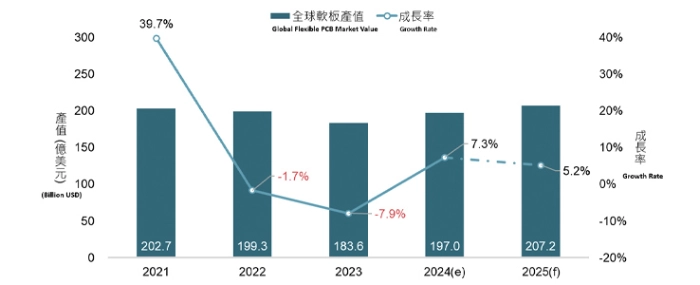
Taiwan Printed Circuit Association (TPCA), together with the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI), forecasts that the global flexible PCB market will gradually recover from the downturn in 2023, with the market size (including rigid-flex PCBs) expected to reach USD 19.7 billion in 2024, representing a 7.3% YoY growth.
As AI applications become more prevalent in the smartphone and computer markets, the demand for flexible PCBs is expected to continue to rise, with the market projected to grow by 5.2% in 2025, reaching USD 20.72 billion, returning to the level seen in 2021.
Over the past few years, the global market for flexible PCBs has experienced significant fluctuations. From 2020 to 2022, the COVID-19 pandemic drove a surge in demand for consumer electronics, which in turn led to rapid growth in the flexible PCB industry. However, with the pandemic-driven boom fading, inventory adjustments in the end market, and global economic uncertainties, the global flexible PCB market saw a significant decline in 2023, shrinking by 7.9% from the previous year to USD 18.36 billion. Nevertheless, the global flexible PCB market has grown steadily over the last five years, rising from USD 13.0 billion in 2019 to USD 18.36 billion in 2023, representing an 8.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The market share of flexible PCBs in the global PCB industry also increased from 20.4% in 2019 to 24.6% in 2023.
In terms of vendor capital types, Taiwanese companies are the largest suppliers of flexible PCBs, accounting for around 34.5% of total market value, followed by Japan and China. Vendors from these three areas account for over 90% of the global flexible PCB market. Looking at individual companies, the top five flexible PCB manufacturers in 2023 were Taiwan's Zhen Ding Technology (19.5%), China's Dongshan Precision (14.4%), Japan's Mektron (14.0%), South Korea's BH (6.7%), and Taiwan's Flexium Interconnect (5.7%). These five companies collectively hold a 60% share of the global market.
Despite a market slowdown in 2023 owing to reduced consumer spending, most flexible PCB makers have remained committed to capital expenditures, capacity expansion, and technology improvements to fulfil future market demand.
Future development in the flexible PCB sector will continue to focus on smartphone applications (such as AI smartphones and foldable phones) and automotive applications. Regarding expansion into Southeast Asia, unlike PCB rigid board manufacturers, flexible PCB manufacturers are mostly taking a "wait-and-see" approach to overseas expansion.
Companies currently planning to set up factories in Southeast Asia include Taiwan's Career Technology, Flexium Interconnect, and Zhen Ding Technology (primarily for rigid board production), Japan's Nitto Denko, China's Dongshan Precision, and South Korea's BH, as well as raw material suppliers such as Taiflex Scientific. Overall, Japanese companies continue to dominate Southeast Asia's flexible PCB industry, with Thailand and Vietnam acting as the region's primary manufacturing centres.
Although the market forecast is positive, the flexible PCB industry confronts hurdles. Notably, the European Union intends to ban the use of PFAS chemicals by 2025, which impact the development of flexible PCB materials, particularly high-frequency materials. Although the regulation of PFAS presents challenges, it also offers new business opportunities. Since advanced high-frequency materials are mainly monopolized by a few suppliers from the U.S. and Japan, the PFAS ban may drive downstream customers to seek PFAS-free materials, providing a rare opportunity for new entrants to penetrate the high-end materials market.

